The average human brain is remarkably energy-efficient.
It's 75% water. It requires food, water and a daily charge.
It requires about 20 watts of power to function and consists of about 86 billion neurons, which communicate through trillions of connections called synapses..
This energy consumption is constant, regardless of whether you are awake and solving complex problems or asleep and dreaming.
The brain's energy usage accounts for approximately 20% of the body's total energy expenditure, despite the brain making up only about 2% of the body's mass.
Our brain is a super computer.Our brain is like a dynamic library that calls up different information based on
- our focus
- our goals.
The brain is a map.
It is plastic.
That means it can change.
It's powered by electricity.
It's the activity of the neurons.
The brain needs to charge.
Charging is sleep.
The shorter you charge, the shorter your life span.
Sleep deprivation is a form of torture.
It causes permanent physical and mental harm.
Humans are the only species that deliberately deprive themselves of sleep without legitimate gain.
The physical and mental impairments caused by one night of bad sleep dwarf those caused by an equivalent absence of food or exercise.
Treat Your Brain Like a Rechargeable Laptop
The brain's battery charge cycle is sleep.
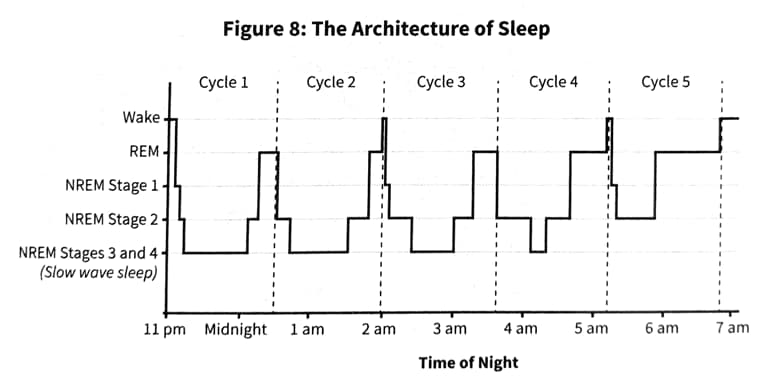
Here is our laptops battery charge cycle.
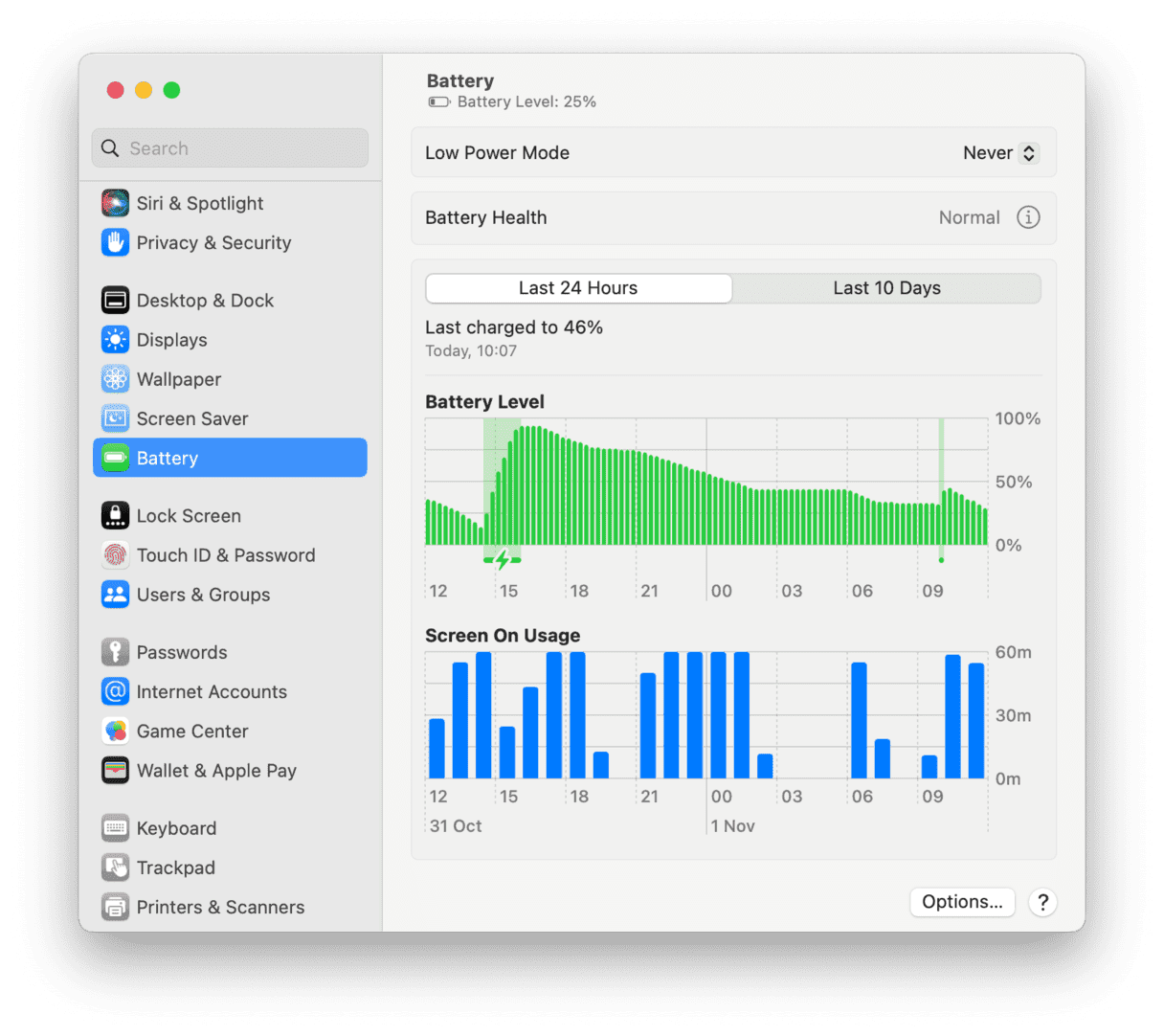
You must keep a charge.
It's similar to driving an electric car, or owning an iPhone.
It comes down to sleeping and getting a high amount of rapid eye movement sleep.
REM is a state in sleep when our body is completely paralyzed and the brain is extremely active.
REM sleep is when you consolidate your memories, your learnings, your emotions and your experiences.
Your Brain is a Computer — It needs to Charge
If you're familiar with computers, you know there is RAM (random access memory) and a hard drive or solid state drive.
RAM short term access. It lets things load up quickly but it will not be there forever.
Hard drive is long term access. It allows the computer to retrieve information forever.
Our brains are similar.
Our hippocampus is the RAM.
Our cortex is the hard drive.
NREM Sleep is the Save Button for the Brain
We obtain most of our deep NREM sleep early in the night, and much of our REM sleep late in the night.
Sleep before learning refreshes our ability to initially make new memories.
It does so each and every night.
While we are awake, the brain is constantly acquiring and absorbing novel information.
Sleep restores the brain's capacity for learning, making room for new memories.
Sleep is like clicking the "save" button.
It protects newly acquired information against forgetting.
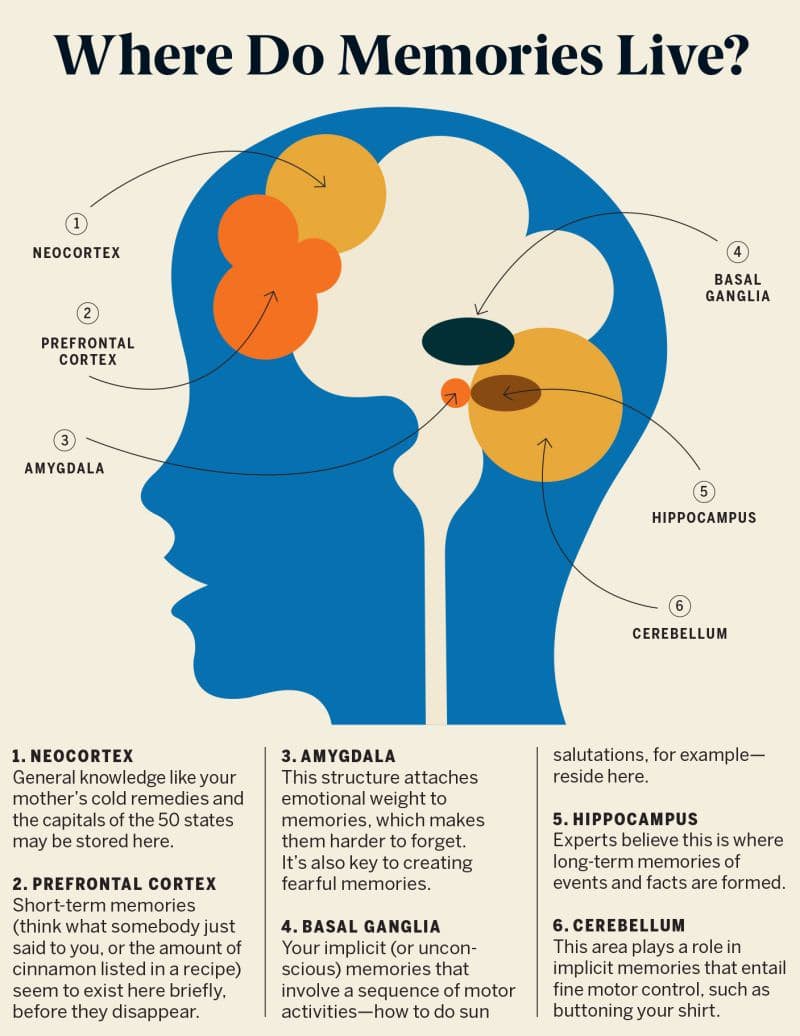
Your Computer Gets Better Specs with More Sleep
When researchers correlated the intervening sleep stages with the number of facts retained the following morning, deep NREM sleep carried the vote: the more deep NREM sleep, the more information an individual remembered the next day
It turns out that those information packets were being recalled from very different geographical locations within the brain at the two different times. Before having slept, participants were fetching memories from the short-term storage site of the hippocampus — that temporary warehouse, which is a vulnerable place for any long duration of time if you are a new memory. But things looked very different by the next morning. The memories had moved.
This is a passage from the book Why We Sleep by Matthew Walker.
Those with increased NREM sleep had 20 and 40 percent memory retention benefit.
Your Brain's Need for Sleep and it's Effect on Weight
The less you sleep the more you are likely to eat.
In these two ways, sleeping less than seven or eight hours a night will increase your probability of gaining weight, being overweight, or being obese and significantly increases your likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
The global health cost of diabetes is $375 billion a year. That of obesity is more than $2 trillion.
Diabetes lops ten years off an individual's life expectancy and cost $85,000 per patient.
Short sleep causes the body to deplete muscle mass and retain fat.
A desire for heavy-hitting carb rich foods (bread, pasta) and salty snacks (potato chips and pretzels) all increased by 30-40% when sleep was reduced by several hours. Less affected were protein-rich foods (meat and fish).
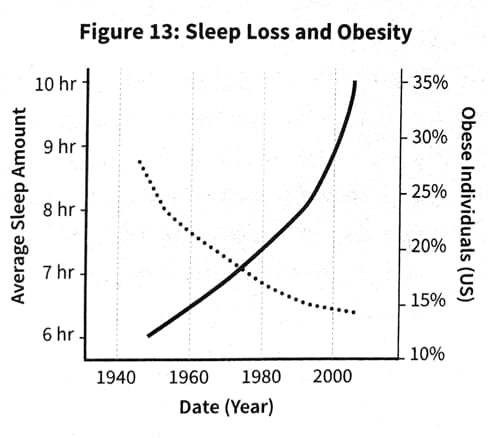
Based on evidence gathered over the past 30 years, the epidemic of insufficient sleep is very likely a key contributor to the epidemic of obesity. Epidemiological studies have established that people who sleep less are the same individuals who are more likely to be overweight or obese.
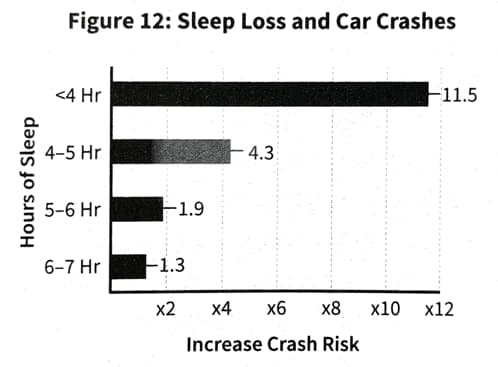
Sleep Deprivation Causes Serious Harm
- Vehicle accidents caused by drowsy driving exceed those caused by alcohol and drugs combined.
- Wakefulness is low-level brain damage, while sleep is neurological sanitation.
- Getting too little sleep across the adult life span will significantly raise your risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
- Unhealthy sleep, unhealthy heart.
- Adults 45+ who sleep < 6 hours are 200% more likely to have a heart attack or stroke compared to those sleeping 7-8 hours.
- Men who suffer from sleep disorders (sleep apnea and snoring) have significantly lower levels of testosterone.
Avoid Sleeping Pills. You Wouldn't swap a MacBook Battery out for a Duracel.
- Sleep pills almost always do more harm than good.
- The quality of pill-induced sleep is deficient.
- Sleep pills are addictive.
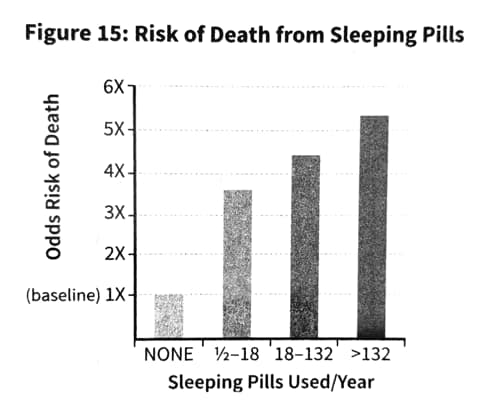
- Individuals using prescription sleep medications are significantly more likely to die and to develop cancer than those who do not.
Avoid Coffee After 4pm
1 dose of caffeine in the evening decreases 20% decrease in deep sleep.
Andrew Huberman's Guide on How to Get a Better Sleep (Charge)
Phase 1: Waking and Early Morning (Hours 1-4):
Get morning sunlight immediately
- Outdoor light exposure causes a beneficial cortisol peak early in the morning; increases daytime mood, energy and alertness; and helps you fall asleep more easily at night 1.
A morning walk outdoors can provide you with both light exposure and optic flow, which quiets activity of the amygdala and related circuits and reduces feelings of stress and anxiety all day.
- Delay coffee 90 minutes in the morning
- Drink 32 Oz of water when you wake up. Add a pinch of sea salt for a source of electrolytes.
- If it's dark when you wake up, turn on all your lights
- Do not wear blue blockers during the day
Phase 2: Midday Through Evening (Hours 5–13)
Eat a lower-carb lunch to help avoid an afternoon crash. Go for a short 5–30 minute walk after lunch to increase metabolism and further calibrate your circadian rhythm with light exposure.
Eat dinner and prioritize sunset light exposure.
Phase 3: Bedtime and Sleeping (Hours 14-24)
Start dimming the lights shortly after sunset and avoid overhead and bright lights in general.
- Cool your bedroom 1-3 degrees lower than usual.
- Make your room as dark as possible using blackout blinds or an eye mask.
Dr. Matthew Walker's Guide on How to Get a Better Sleep (Charge)
Sources